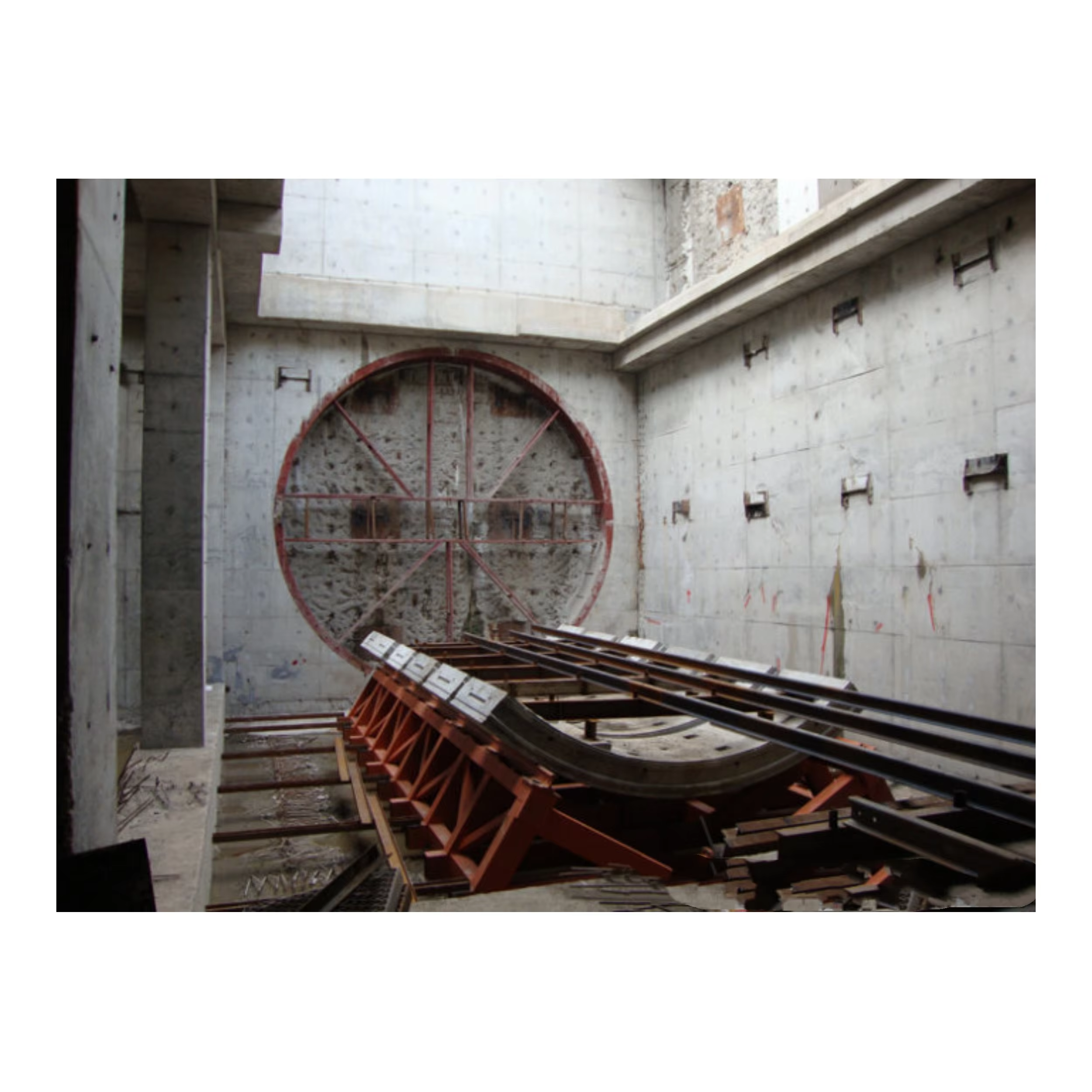
Shield tunneling technology has revolutionized underground construction projects worldwide, enabling the efficient excavation of tunnels for metros, highways, and utility systems. However, the demanding operational environment of shield machines subjects various components to extreme wear and tear, making the identification and management of wear parts crucial for project success. Understanding which components require regular replacement and maintenance is essential for tunnel construction professionals to minimize downtime, control costs, and ensure safety throughout the excavation process.
Primary Cutting Tool Components
Cutter Heads and Disc Cutters
The cutter head represents the most critical wear component in any shield machine, directly interfacing with the excavation face and bearing the brunt of cutting forces. Disc cutters, which are mounted on the cutter head, experience continuous contact with rock and soil formations, leading to predictable wear patterns that require systematic replacement. The wear rate of these components depends heavily on geological conditions, with harder rock formations accelerating degradation significantly compared to softer soil conditions.
Modern disc cutters incorporate advanced metallurgy and heat treatment processes to extend service life, but even the most durable designs require replacement after excavating specific distances. Monitoring systems now track individual cutter performance, allowing operators to schedule replacements based on actual wear rather than estimated intervals. This precision approach to cutter management has become a cornerstone of efficient tunneling operations.
Peripheral Cutting Tools
Beyond the primary disc cutters, shield machines employ various peripheral cutting tools that address specific excavation challenges. These include copy cutters for maintaining tunnel diameter, face scrapers for material management, and specialized tools for handling mixed ground conditions. Each tool type experiences distinct wear patterns based on its function and position within the cutting system.
The replacement frequency of peripheral cutting tools varies considerably depending on ground conditions and operational parameters. Abrasive soils can rapidly wear scraper tools, while highly fractured rock may damage copy cutters through impact loading. Effective maintenance programs account for these variations by maintaining adequate spare inventories and implementing condition-based replacement strategies.
Sealing and Protection Systems
Main Bearing Seals
The main bearing system that supports cutter head rotation requires sophisticated sealing arrangements to prevent contamination and maintain lubrication integrity. These seals operate in challenging conditions, exposed to abrasive particles, high pressures, and temperature variations that gradually compromise their effectiveness. Regular inspection and replacement of main bearing seals prevents costly bearing failures that could halt tunneling operations for extended periods.
Advanced seal designs now incorporate multiple barrier systems and condition monitoring capabilities that provide early warning of seal degradation. However, even with these improvements, shield machine wear parts in sealing systems require scheduled replacement to maintain operational reliability. The cost of seal replacement is minimal compared to the potential consequences of seal failure and subsequent bearing damage.
Chamber Pressure Seals
Pressure balance shield machines rely on sophisticated sealing systems to maintain chamber pressure and prevent ground water ingress or pressure loss. These seals must accommodate the rotational movement of the cutter head while maintaining pressure differentials that can exceed several bars. The demanding operating environment subjects these seals to continuous flexing, abrasion, and chemical exposure from ground water and conditioning agents.
Modern chamber seals incorporate redundant sealing elements and monitoring systems that track seal performance in real-time. Despite these advances, seal replacement remains a regular maintenance activity that requires careful planning to minimize interruptions to the tunneling schedule. Understanding seal wear patterns enables project teams to optimize replacement intervals and maintain spare parts inventories appropriately.

Material Handling Components
Screw Conveyor Elements
The screw conveyor system responsible for removing excavated material experiences significant wear due to the abrasive nature of soil and rock particles. The conveyor flights, which move material from the excavation chamber to the surface, gradually wear down through continuous contact with abrasive materials. This wear is particularly pronounced when tunneling through sandy or gravelly soils that act like grinding compounds on the steel surfaces.
Replacement of screw conveyor flights requires careful scheduling to minimize impact on production rates, as the conveyor system is critical for maintaining face pressure and preventing ground settlement. Advanced wear-resistant materials and coatings have extended flight life significantly, but regular replacement remains necessary for sustained operations. Monitoring wear patterns helps optimize replacement timing and identify opportunities for material improvements.
Muck Handling System Components
Beyond the screw conveyor, various components within the material handling system experience wear that requires attention. These include gate valves, chutes, and transfer mechanisms that direct excavated material through the shield machine. Abrasive wear, impact damage, and corrosion all contribute to component degradation that must be managed through systematic replacement programs.
The wear rate of muck handling components varies significantly based on soil characteristics and operational practices. Sticky clay soils can cause buildup that leads to mechanical wear and blockages, while rocky conditions may cause impact damage to transfer chutes and gate mechanisms. Effective maintenance strategies account for these variations by tailoring replacement intervals to actual operating conditions rather than fixed schedules.
Drive and Propulsion Elements
Thrust Cylinder Seals
The hydraulic thrust cylinders that propel the shield machine forward operate under extreme conditions, with seals subjected to high pressures, contamination, and continuous cycling. These seals prevent hydraulic fluid leakage while maintaining the precise force control necessary for safe tunneling operations. Seal degradation can lead to reduced thrust capacity, contamination of surrounding soil, and potential safety hazards.
Modern thrust cylinder designs incorporate advanced seal materials and configurations that extend service life significantly compared to earlier systems. However, the demanding operating environment still necessitates regular seal replacement to maintain system reliability. Condition monitoring systems now track cylinder performance and provide early warning of seal degradation, enabling proactive maintenance scheduling.
Articulation Joint Components
Shield machines employ articulation joints to navigate curves and maintain alignment with the designed tunnel path. These joints incorporate various wear components including bushings, seals, and bearing surfaces that experience continuous loading and movement. The wear rate of articulation components depends heavily on the tunnel alignment requirements and the frequency of steering corrections during excavation.
Replacement of articulation joint components requires careful coordination with tunneling operations, as these systems are critical for maintaining tunnel geometry. Advanced joint designs now incorporate self-lubricating materials and improved seal arrangements that extend service life. However, regular inspection and replacement of wear components remains essential for reliable steering performance and tunnel quality.
Monitoring and Optimization Strategies
Condition-Based Maintenance
Modern shield machines incorporate extensive monitoring systems that track the performance and condition of critical wear components in real-time. These systems measure parameters such as vibration, temperature, pressure, and torque to identify developing problems before component failure occurs. Condition-based maintenance strategies use this data to optimize replacement intervals and minimize unnecessary downtime.
The implementation of condition monitoring has transformed wear parts management from reactive to predictive maintenance approaches. This shift enables project teams to schedule replacements during planned maintenance windows rather than responding to unexpected failures. The result is improved project efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced safety through better component reliability.
Spare Parts Management
Effective management of spare parts inventory is crucial for maintaining shield machine availability and controlling project costs. The high value and long lead times associated with many shield machine wear parts necessitate careful planning to ensure adequate supplies without excessive inventory carrying costs. Advanced inventory management systems now use wear rate data and production schedules to optimize spare parts ordering and storage.
The geographic isolation of many tunneling projects adds complexity to spare parts management, as emergency deliveries may be impossible or prohibitively expensive. Successful projects maintain strategic spare parts inventories based on statistical analysis of component failure rates and operational requirements. This approach balances inventory costs against the risk of project delays due to parts shortages.
FAQ
How often should disc cutters be replaced during shield tunneling operations
Disc cutter replacement intervals depend on geological conditions, with typical ranges from 200 to 2000 meters of excavation per cutter in rock conditions. Softer ground may allow longer intervals, while highly abrasive formations require more frequent replacement. Modern monitoring systems track individual cutter performance to optimize replacement timing based on actual wear rather than fixed intervals.
What factors influence the wear rate of shield machine sealing systems
Seal wear rates are influenced by ground water chemistry, abrasive particle content, operating pressures, and temperature conditions. High groundwater pressure and abrasive soils accelerate seal degradation, while proper conditioning agents and operational practices can extend seal life. Regular monitoring of seal performance indicators helps identify optimal replacement timing.
How can tunneling contractors minimize wear parts costs without compromising safety
Cost optimization strategies include implementing condition-based maintenance programs, using advanced materials and coatings, optimizing operational parameters, and maintaining strategic spare parts inventories. Regular training of maintenance personnel and investment in monitoring systems can significantly reduce total wear parts costs while maintaining safety standards throughout the project.
What role does geological investigation play in wear parts planning
Comprehensive geological investigation enables accurate prediction of wear rates and component life expectancy, allowing for more precise spare parts planning and budget allocation. Understanding ground conditions helps select appropriate cutting tools, optimize machine configuration, and establish realistic replacement schedules that align with project timelines and budget constraints.