Understanding Modern Steel Factory Building Solutions
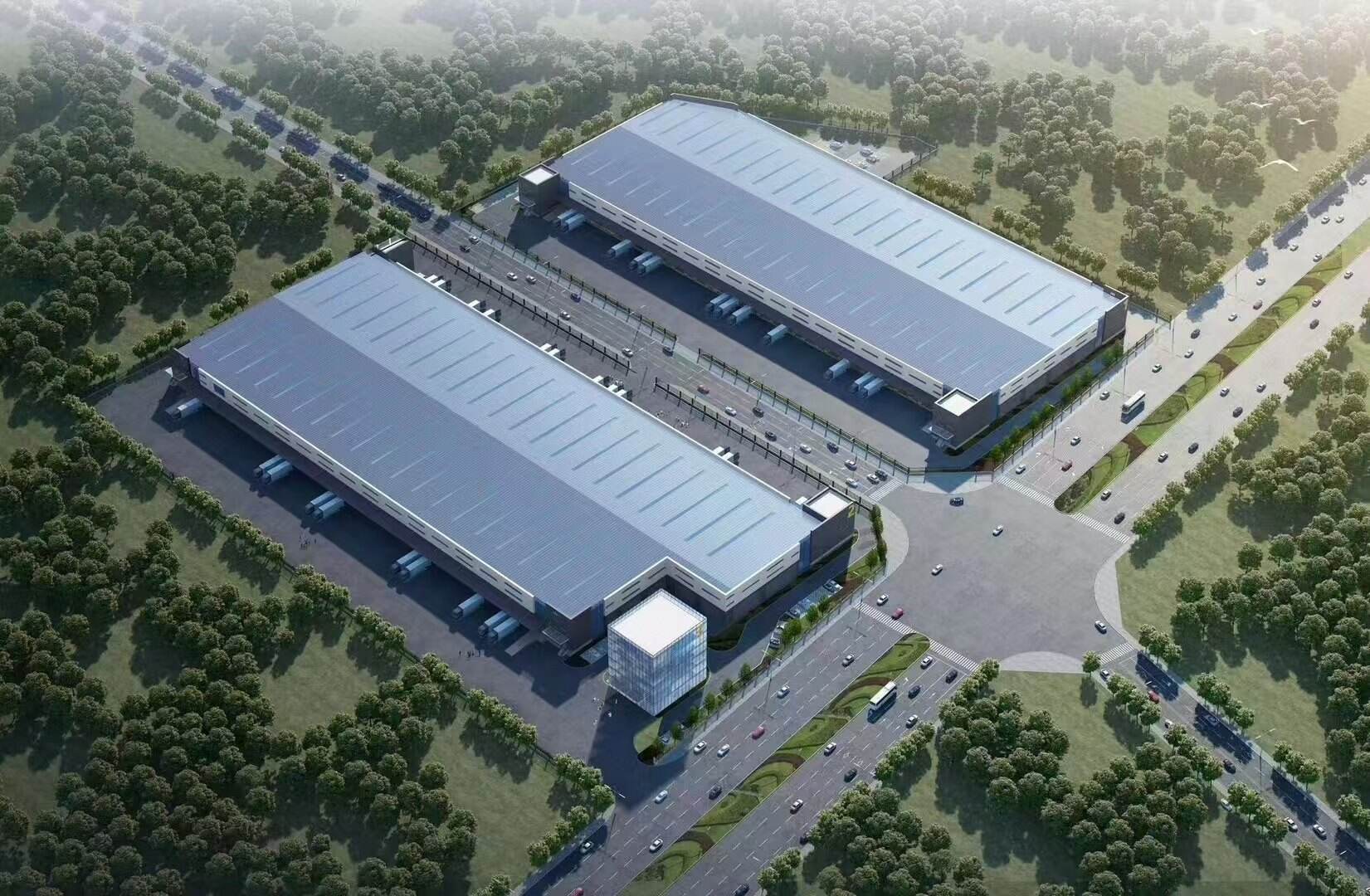
Steel factory buildings have revolutionized industrial construction, offering unparalleled flexibility and customization options for businesses across various sectors. These robust structures combine architectural innovation with practical functionality, creating spaces that perfectly align with specific manufacturing and operational requirements. The customization process of steel factory buildings involves multiple crucial elements, from initial design considerations to final implementation, ensuring each facility meets its intended purpose effectively.
Design and Planning Phase
Initial Assessment and Requirements Analysis
The customization journey begins with a comprehensive assessment of the client's specific needs. This crucial phase involves analyzing production workflows, equipment specifications, and spatial requirements. Engineers and architects collaborate to understand the intended use of steel factory buildings, considering factors such as material handling systems, production line layouts, and future expansion possibilities. This thorough evaluation forms the foundation for a successful customization project.
During this stage, experts also evaluate environmental conditions, local building codes, and zoning regulations. These considerations help determine the optimal building dimensions, structural requirements, and necessary modifications to ensure compliance while maintaining operational efficiency. The assessment phase typically includes detailed discussions about budget constraints and timeline expectations, allowing for realistic project planning.
Structural Engineering Considerations
Steel factory buildings require precise engineering calculations to ensure structural integrity while accommodating customization requirements. Engineers analyze load-bearing capacities, wind resistance, and seismic considerations specific to the building's location. The structural design must account for specialized equipment weight, overhead crane systems, and potential future modifications.
The selection of appropriate steel grades and components plays a vital role in the customization process. Engineers carefully calculate column spacing, truss designs, and foundation requirements to create a structure that perfectly balances strength, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. This attention to detail ensures the longevity and reliability of the customized facility.
Customization Elements and Features
Building Envelope Solutions
The building envelope represents a critical aspect of steel factory buildings customization. Modern facilities often incorporate advanced insulation systems, vapor barriers, and energy-efficient cladding materials. These elements are carefully selected based on local climate conditions, interior climate control requirements, and energy efficiency goals.
Customization options for the building envelope extend to wall panels, roofing systems, and exterior finishes. Manufacturers can choose from various materials and designs that not only provide protection from the elements but also contribute to the facility's overall aesthetic appeal and energy performance. The integration of natural lighting through strategic placement of windows, skylights, and translucent panels further enhances the building's functionality.
Interior Space Optimization
The interior layout of steel factory buildings demands careful consideration to maximize operational efficiency. Customization includes the strategic placement of columns, the design of mezzanine levels, and the integration of specialized areas such as office spaces, storage zones, and maintenance facilities. The floor plan must accommodate current production requirements while maintaining flexibility for future modifications.
Height clearances, bay spacing, and access points are customized to suit specific equipment and workflow requirements. Modern steel factory buildings often incorporate advanced ventilation systems, specialized lighting solutions, and efficient utility distribution networks. These elements are carefully integrated into the design to create an optimal working environment.
Technical Integration and Systems
Mechanical and Electrical Systems
The customization of steel factory buildings extends to sophisticated mechanical and electrical systems integration. HVAC systems are designed to maintain specific temperature and humidity levels required for manufacturing processes. Electrical systems must support heavy machinery, automated equipment, and advanced control systems while meeting safety standards and energy efficiency goals.
Power distribution, lighting controls, and communication networks are carefully planned and integrated into the building's structure. The design includes provisions for backup power systems, emergency lighting, and future technological upgrades. These systems are configured to optimize energy consumption and maintain operational continuity.
Safety and Compliance Features
Safety considerations play a paramount role in customizing steel factory buildings. The design incorporates fire suppression systems, emergency exits, and safety barriers according to industry standards and local regulations. Specialized ventilation systems may be required for facilities handling specific materials or processes.
Access control systems, security features, and monitoring equipment are integrated into the building's design. Loading docks, personnel entries, and emergency evacuation routes are strategically planned to ensure safe and efficient movement of people and materials. These safety features are customized based on the facility's specific operational requirements and risk assessments.

Construction and Implementation Process
Site Preparation and Foundation Work
The implementation of customized steel factory buildings begins with thorough site preparation. This includes soil testing, grading, and foundation design specific to the building's requirements and local conditions. The foundation system is engineered to support the structure's weight, equipment loads, and anticipated operational stresses.
Construction teams coordinate the installation of underground utilities, drainage systems, and other infrastructure elements before beginning the steel erection process. This careful preparation ensures a stable foundation for the customized facility and prevents future structural issues.
Assembly and Quality Control
The assembly of steel factory buildings follows a precise sequence, with each component manufactured to exact specifications. Quality control measures are implemented throughout the construction process, from material inspection to final assembly verification. Specialized crews work with advanced equipment to ensure accurate placement and connection of structural elements.
Regular inspections and testing during construction verify that all customized features meet design specifications and building codes. This attention to detail during implementation ensures the finished facility performs as intended and provides long-term value for the owner.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors influence the customization cost of steel factory buildings?
The customization cost is influenced by several factors including building size, complexity of design features, material selection, site conditions, and specific equipment integration requirements. Additional considerations include local building codes, climate conditions, and the level of automation needed in the facility.
How long does it typically take to complete a customized steel factory building?
The timeline for completing steel factory buildings varies depending on the project's scope and complexity. Generally, the process from initial design to final completion can take anywhere from 6 to 18 months. This includes planning, permitting, manufacturing, and construction phases.
Can existing steel factory buildings be modified for changing needs?
Yes, steel factory buildings are inherently adaptable and can be modified to accommodate changing operational requirements. Modifications may include expansions, interior reconfigurations, or systems upgrades. However, any changes must be carefully planned and engineered to maintain structural integrity and comply with building codes.